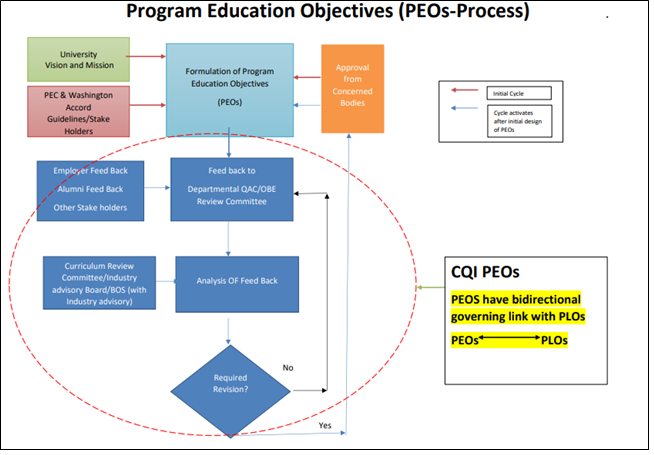
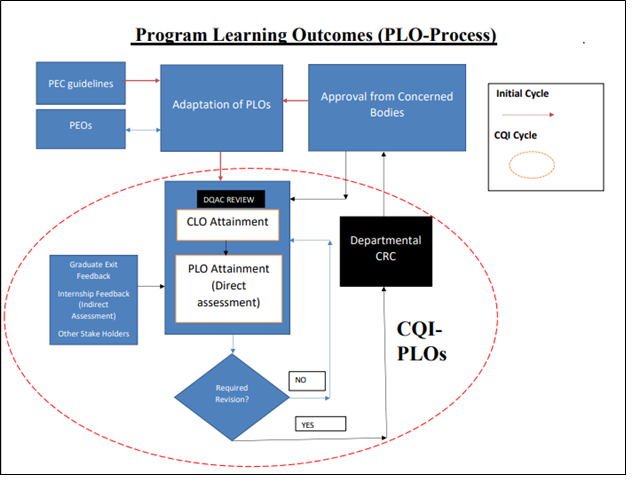
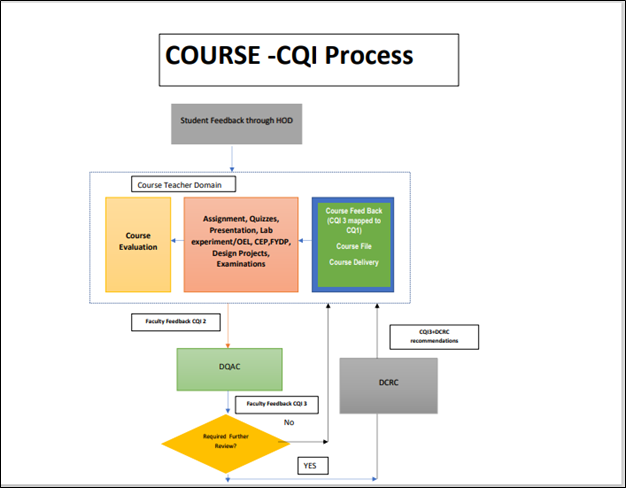
- About
The Islamia University of Bahawalpur is a public sector university in Bahawalpur, Pakistan, which was originally established by His Highness Nawab Sir Sadiq Muhammad Khan Abbasi - V as the Jamia Abbasia in 1925.
Read more - Administration
A Vice Chancellor's Secretariat is also functioning in the IUB to extend multiple services to the Public, students, faculty members and employees of the University. As it is under the direct supervision of the Vice Chancellor, it has to form policy matters of the IUB and monitor the implementation of the same.
View All - Academics
The office also coordinates with teaching departments for review and update of infrastructure including laboratories and classrooms, planning and execution of trainings for faculty, and internships / teaching
Read more - Admissions
Bahawalpur has always been a seat of higher learning. Uch Sharif (a nearby ancient town) had one of the largest universities in the world where scholars from all over the world used to come for studies.
Read more - Campuses
A Historical building was initially constructed by His Highness Nawab Sir Sadiq Muhammad Khan Abbasi – V in the heart of the city near Government Sadiq Egerton College at University Chowk, Bahawalpur, to impart higher education in 1950.
Read moreThe Islamia University of Bahawalpur established Bahawalnagar Sub-Campus in 2005. The Campus is located on Minchanabad road Bahawalnagar scattered over 50 acres of land.
Read moreThe Islamia University of Bahawalpur established Rahim Yar Khan Sub-Campus in 2005. The Campus is located on Abu Dhabi Road Rahim Yar Khan scattered over 80 acres of land.
Read moreInitially university started at the Abbasia Campus and Khawaja Farid Campus with ten departments. Later, 1280 acres of land
Read more - Campus Life
The Islamia University of Bahawalpur is a public sector university in Bahawalpur, Pakistan, which was originally established by His Highness Nawab Sir Sadiq Muhammad Khan Abbasi - V as the Jamia Abbasia in 1925.
Read more - Publications
Corps Commander Bahawalpur visits the Islamia University of Bahawalpur | National Seminar on Food Security | IUB and Sichuan Agriculture University’s Project included in the CPEC | IUB announces Scholarahips for the Children of Martyrs of Bahawalpur Police
Read moreHonourable Chief Minister Punjab visits IUB stalls at Bahawalpur Trade Fair | Federal Minister of State Zartaj Gul visits IUB | Ground Breaking Ceremony of 2.5 MW Solar Park at IUB
Read moreFederal Minister for National Food Security Visits IUB Agriculture Farm. | Additional IG Police South Punjab Visits IUB. | MD Pakistan Bait ul Mal Visits IUB.
Read more
About
- About University
- Bahawalpur - The City
- Vice Chancellor Message
- Vision & Mission
- Rankings
- Governance
- Former Vice Chancellors
- Notable Alumni
Administration
- Vice Chancellor Office
- Registrar Office
- Accounts Division
- Audit Division
- Directorate of Outreach, Communications and Public Relations
- Directorate of IT
- Directorate of Engineering
- Directorate of Academics
- Directorate of Affiliation
- Directorate of Alumni Affairs
- Directorate of AS&RB
- Directorate of Culture and Heritage Research Center (CHRC)
- Directorate of Financial Assistance
- Directorate of International Linkages
- Directorate of Land Records
- Directorate of Planning and Development
- Directorate of Private Students
- Directorate of QEC
- Directorate of Sports
- Directorate of Student Affairs
- Directorate of Sustainable Tourism
- Library
- Senior Tutor Office
- Executive Training Center
- Office of Research, Innovation and Commercialization
- Medical and Health Division
- Security Systems Division
- University Guest House
- Motor Transport Division
Academics
- Faculties & Departments
- Academic Programs
- University Colleges
- Research
- Journals
- Chairs
- Scholarships
- Academic Calendar
Admissions
- Why IUB?
- Admissions
- Important Dates
- Eligibility Criteria
- Merit Determination
- Reserved Seats
- How to Apply Admission / Test
- Faq's
- Admission Queries / Contact
Campuses
- Abbasia Campus
- Baghdad-ul-Jadeed Campus
- Khawaja Fareed Campus
- Bahawalnagar Campus
- Rahim Yar Khan Campus
Campus Life
- IUB Student Societies
- Cultural Festivals
- Campus Facilities
- University Transport
- Sports and Physical Activities
- Events and Days Celebrations
- Residential and Hostel Facilities
- Special Students Facilitation Center
- Student Support